Multiple critical vulnerabilities in the popular n8n open-source workflow automation platform allow escaping the confines of the environment and taking complete control of the host server.
Collectively tracked as CVE-2026-25049, the issues can be exploited by any authenticated user who can create or edit workflows on the platform to perform unrestricted remote code execution on the n8n server.
Researchers at several cybersecurity companies reported the problems, which stem from n8n’s sanitization mechanism and bypass the patch for CVE-2025-68613, another critical flaw addressed on December 20.
According to Pillar Security, exploiting CVE-2026-25049 enables complete compromise of the n8n instance and could be leveraged to run arbitrary system commands on the server, steal all stored credentials, secrets (API keys, OAuth tokens), and sensitive configuration files.
By exploiting the vulnerability, the researchers were also able to access the filesystem and internal systems, pivot to connected cloud accounts, and hijack AI workflows (intercept prompts, modify responses, redirect traffic).
As n8n is a multi-tenant environment, accessing internal cluster services can potentially allow pivoting to other tenants’ data.
“The attack requires nothing special. If you can create a workflow, you can own the server,” Pillar Security says in a report today.
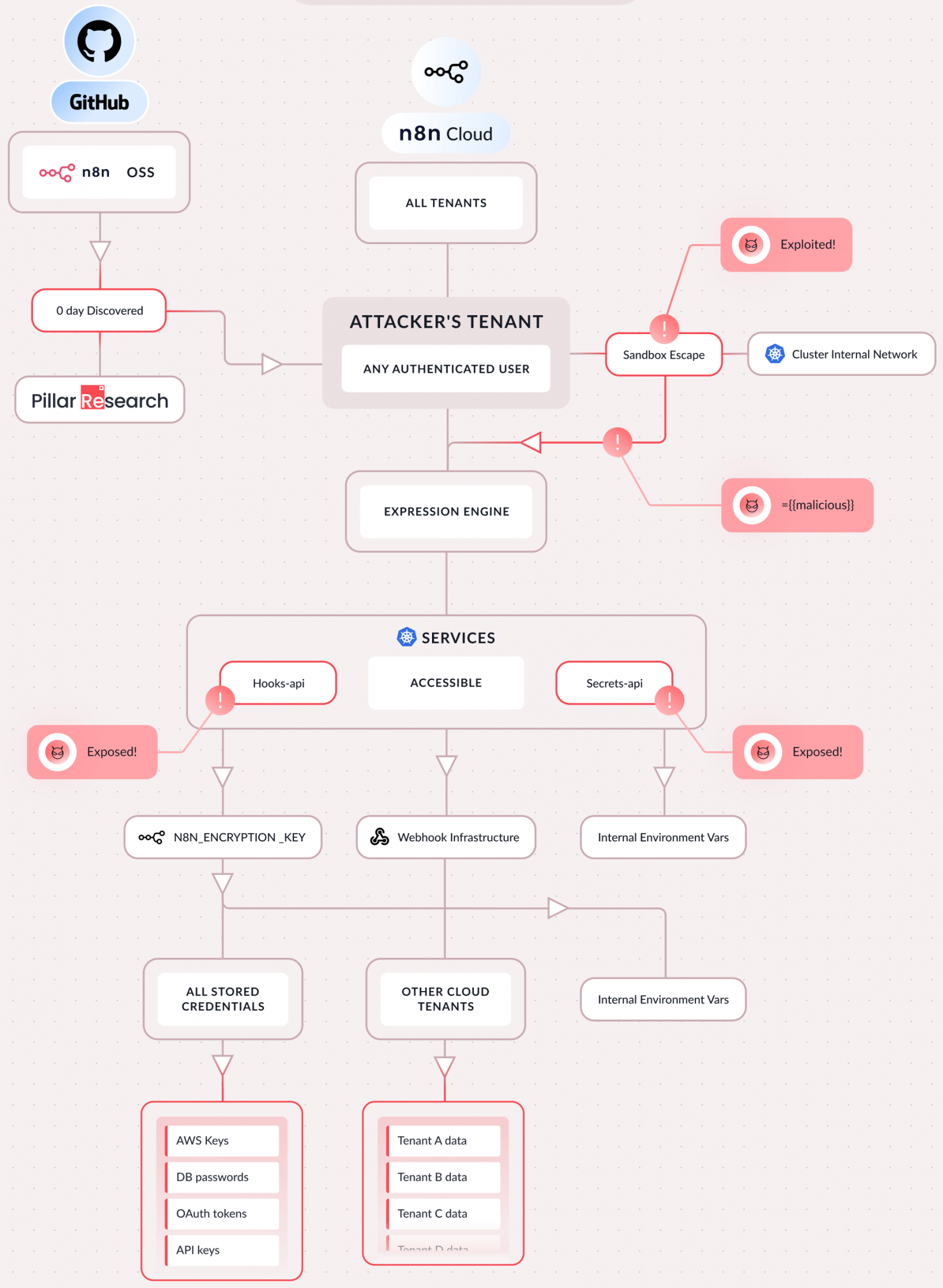
Source: Pillar Security
Pillar’s report describes the problem as incomplete AST-based sandboxing and explains that it arises from n8n’s weak sandboxing of user-written server-side JavaScript expressions in workflows.
On December 21, 2025, they demonstrated a chained bypass to the n8n team, allowing sandbox escape and access to the Node.js global object, leading to RCE.
A fix was implemented two days later, but upon further analysis, Pillar found it incomplete, and a second escape via a different mechanism using equivalent operations remained possible.
n8n developers confirmed the bypass on December 30, and eventually, n8n released version 2.4.0 on January 12, 2026, addressing the issue.
Researchers at Endor Labs also discovered sanitization bypasses and demonstrated the CVE-2026-25049 vulnerability with a simple proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit that achieves remote code execution.
“In all versions prior to 2.5.2 and 1.123.17, the sanitization function assumes keys in property accesses are strings in attacker-controlled code,” says Cristian Staicu of Endor Labs.
However, while the check is reflected in TypeScript typings, it is not enforced at runtime, introducing a type-confusion vulnerability. This leads to bypassing the “sanitization controls entirely, enabling arbitrary code execution attacks.”
In a report today, researchers at SecureLayer7 provide the technical details that enabled them to achieve “server side JavaScript execution using the Function constructor.”
They discovered CVE-2026-25049 while analyzing CVE-2025-68613 and n8n’s fix for it. It took more than 150 failed attempts to refine a successful bypass.
SecureLayer7’s report also includes a PoC exploit and detailed steps for the initial setup and creating a malicious workflow that leads to full server control.
Recommended steps
n8n users should update the platform to the most recent version (currently 1.123.17 and 2.5.2). Pillar security also recommends rotating the ‘N8N_ENCRYPTION_KEY’ and all credentials stored on the server, and reviewing workflows for suspicious expressions.
If updating is not possible at the moment, the n8n team provides administrators with a workaround, which acts as a temporary mitigation and does not completely address the risk:
- Limit workflow creation and editing permissions to fully trusted users only
- Deploy n8n in a hardened environment with restricted operating system privileges and network access to reduce the impact of potential exploitation
Currently, there have not been any public reports about CVE-2026-25049 being exploited. However, n8n’s growing popularity appears to have caught the attention of cybercriminals in the context of the Ni8mare flaw (CVE-2026-21858).
GreyNoise this week reported seeing potentially malicious activity targeting exposed n8n endpoints vulnerable to Ni8mare, logging at least 33,000 requests between January 27 and February 3.
Although this probing could be due to research activity, scanning for the /proc filesystem indicates interest in post-exploitation potential.
The future of IT infrastructure is here
Modern IT infrastructure moves faster than manual workflows can handle.
In this new Tines guide, learn how your team can reduce hidden manual delays, improve reliability through automated response, and build and scale intelligent workflows on top of tools you already use.
Related Articles:
New sandbox escape flaw exposes n8n instances to RCE attacks
Critical sandbox escape flaw found in popular vm2 NodeJS library
Max severity Ni8mare flaw lets hackers hijack n8n servers
GitLab warns of high-severity 2FA bypass, denial-of-service flaws
SolarWinds releases third patch to fix Web Help Desk RCE bug
